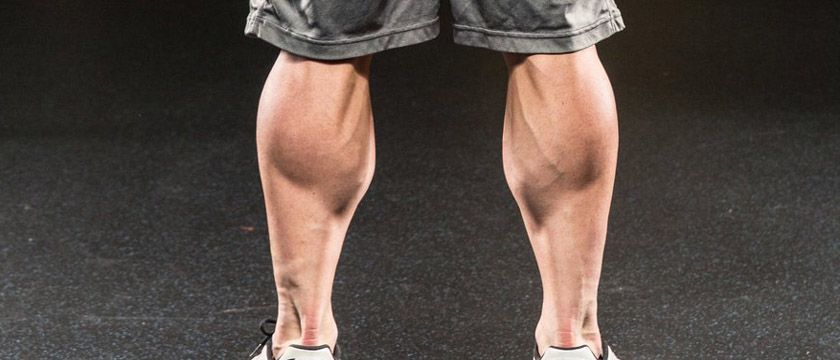
It’s important to develop and strengthen your overall body as every muscle has its own significance. Calf muscle lifts more weights than your pecs and biceps.
Overview of Calf Muscle
The Soleus which is the larger and deeper of the two calf muscles and originates from both the fibula and tibia. Its function is to flex the foot. The calf, like the deltoids and abdominals, a very aesthetic body part. A good pair of calf looks good on the beach or tennis court as well as on the bodybuilding stage. Ideally, your calf development should about equal the development of your biceps. If your calf is smaller than your arms, then you need to give extra attention. The calf is considered the most difficult muscle group in the body to develop. However, you need to train it in different angles to get that massive and dynamic calf.
Training Calf Muscle
The calf is tough and used to a lot of hard work, so the best way to make them grow is to constantly shock them, using every high-intensity training principle possible. Some of the training techniques are listed below:
Standing calf raise
The purpose of performing this technique is to develop an overall mass of the calf.
How to do it: Stand with your toes on the block with barbell (use moderate weight as we need to do isolation movement) on your shoulder. Hook your hand on the barbell and straightens your legs. Lift the weight clear of the support. Lower your heels as far as possible toward the floor, keeping your knees slightly bent throughout the movement into work the lower area of the calf as well as the upper and feeling the calf stretch to the maximum.
Calf raises on the leg press machine
The purpose of performing this technique is to develop the calf muscle.
How to do it: Position yourself, as if to do a leg press, but push against the foot pads only with your toes, leaving your heels unsupported. Straighten your legs and press the weight up until your knees are almost locked out. With your knees just slightly bent, keep your heels pressed upward but let your toes come back toward you, feeling the fullest possible stretch in the calf muscles.
Seated Calf raises
The purpose is to develop lower and outer areas of the calf.
How to do it: Sit on the machine and place your toes on the bottom crosspiece, hooking your knees under the crossbar. Slowly lower your heels as far toward the ground as possible. Then press back up on your toes until your calf is fully contracted. Try not to rock back and forth too much, but keep the calf working with a steady, rhythmic motion.
Donkey calf raise
The purpose is to develop the thickness of the back of the calf.
How to do it: Place your toes on a block, bend forward from the waist and lean on the bench or a table for support or use a donkey calf machine. Your toes should be directly below your hips. Have a training partner add resistance by seating himself across your hips, as far back as possible to keep pressure off the lower back. With your toes pointed straight ahead, lower your heels as far as possible then come back up on your toes until your calf is fully contracted.
Reverse calf raises
The purpose is to develop the front of the lower leg. It separates the inside calf from the outside calf and makes the leg seem much bigger.
How to do it: Stand with your heels on a block, lower your toes as far as you can then lift up, feeling the muscles at the front of the lower leg contract as fully as possible.
Benefits of Calf muscle training
Calf muscle has numerous benefits which we are not aware of and we have specified some of the reported benefits underneath:
- Calf muscle is the combination of two muscles such as gastrocnemius and soleus muscles which play important role in the flexibility of the leg
- Strong calf muscles provide support to toe and knee joints
- You can improve your performance by training calf muscle with isolation and proper training technique
Precautions/Mistakes of Calf muscle training
We all do mistakes and avoid precautions while training calf muscles which can lead to severe injuries. We have specified some of the best precautions and common mistakes underneath:
- Forcibly stretching the calf muscles to get tissues injured in the calf
- Rupturing calf muscle tissues by overtraining or exerting the muscle
- Ideal calf muscle size should be equal to your bicep size